Continuous Integration
Testomat.io allows executing tests on CI from its interface. A single test, suite, test plan, or all tests can be executed automatically on CI.
Currently following CI systems supported:
- Atlassian Bamboo
- BitBucket Pipelines
- Teamcity
- GitHub Actions
- GitLab CI
- Jenkins
- Circle CI
- Azure Pipelines
Testomat.io uses REST API to trigger jobs on external CI systems. IDs of tests or suites can be passed to the job so only a specific test or suite will be executed. The test runner greps all tests by their IDs and executes a subset of tests. Then a report is sent back to Testomat.io via reporter.
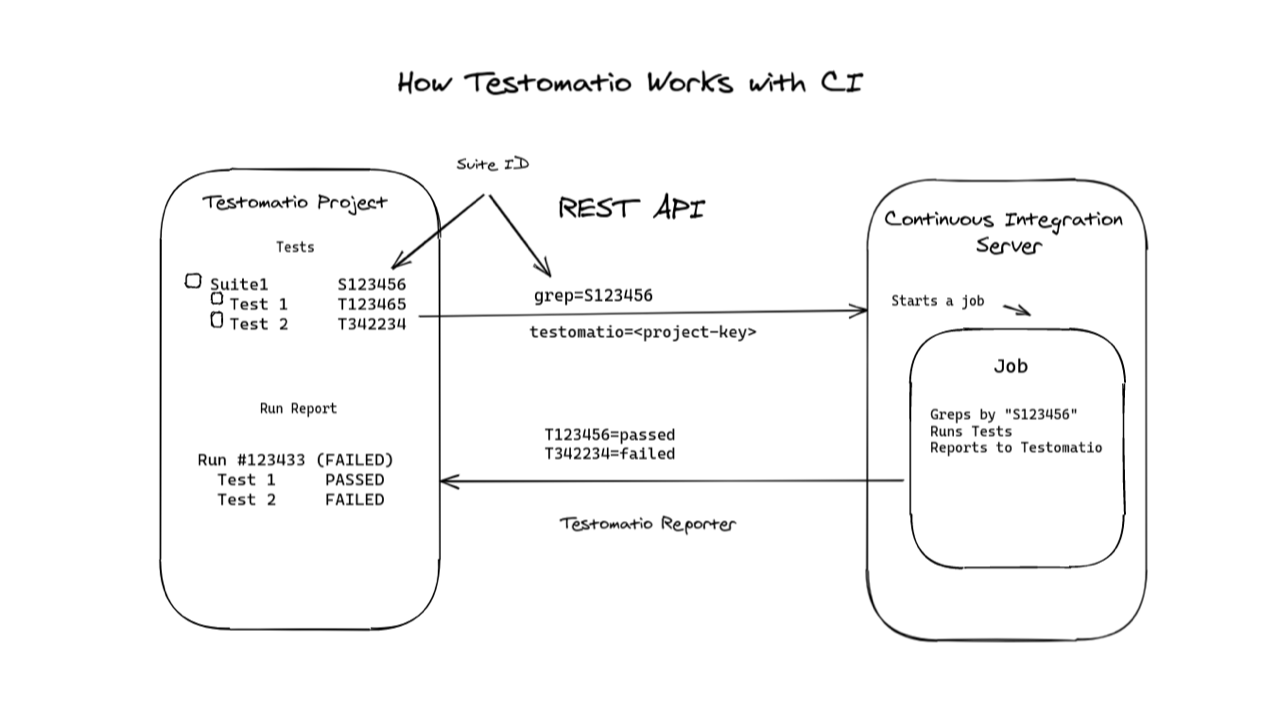
Connecting CI server to Testomat.io consist of the following steps:
- Create Testomat.io Project.
- Import automated tests into that project from a repository.
- Assign IDs for imported tests source code.
- Create a new job in CI according to instructions on this page.
- Connect CI server to Testomat.io.
- Run your tests or suites to get reports!
Configuring CI
Section titled “Configuring CI”CI configuration has 3 steps:
- Establishing a connection with CI.
- Setting up required input variables.
- Setting up custom configuration variables.
Follow the guide for a corresponding CI to set it up.
Input Variables
Section titled “Input Variables”While connection settings can be different across CI settings, the list of input variables is the same.
Here is how run input variable can be accessed on different CIs:
- Atlassian Bamboo:
${bamboo.run} - GitHub Actions:
${github.event.inputs.run}
It may as well pass other input variables which can be used on CI to improve reporting.
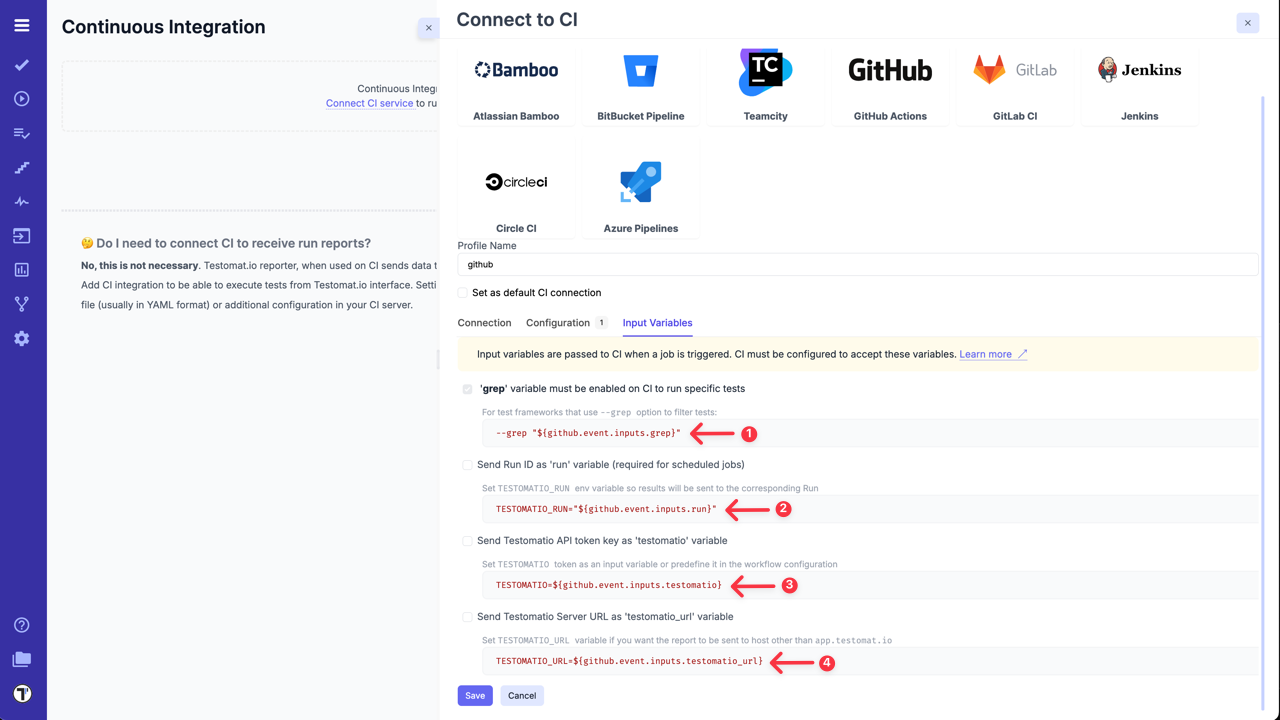
Here is the list of preconfigured input variables:
-
grep- Testomat.io sendsgrepvariable to CI to identify which tests should be executed.grepvariable is required and selected by default in Testomat.io. -
run- passes Run ID to CI. If this option is toggled on, when a run is created in Testomat.io, it is instantly added to the list of runs marked as ‘Scheduled’. On CIrunvariable must be passed asTESTOMATIO_RUNenvironment variable to a reporter. This allows mapping a scheduled run to the run which is currently processed. IfTESTOMATIO_RUNis not set, a duplicate run will be created. -
testomatio- passes project access key to CI. This input variable must be passed asTESTOMATIOenvironment variable to match the Testomat.io project. Toggle on this option if you prefer not to hardcode Testomat.io Project ID in CI configuration but to obtain this value on launch. This may be useful if you have a different Testomat.io project configured on CI run. -
testomatio_url- when working on a self-hosted Testomat.io instance, this variable can be used to pass Testomat.io endpoint to CI system. Passtestomatio_urlenvironment variable toTESTOMATIO_URL.
Environment Configuration
Section titled “Environment Configuration”Sometimes extra configuration is required for CI job. For instance, extra configuration variables can be used to specify:
- browser.
- target branch.
- staging/production environments.
- suites.
Testomat.io allows to predefine configuration variables and adjust them for each run. Config variables can be set in ‘Configuration’ tab on CI connection settings.
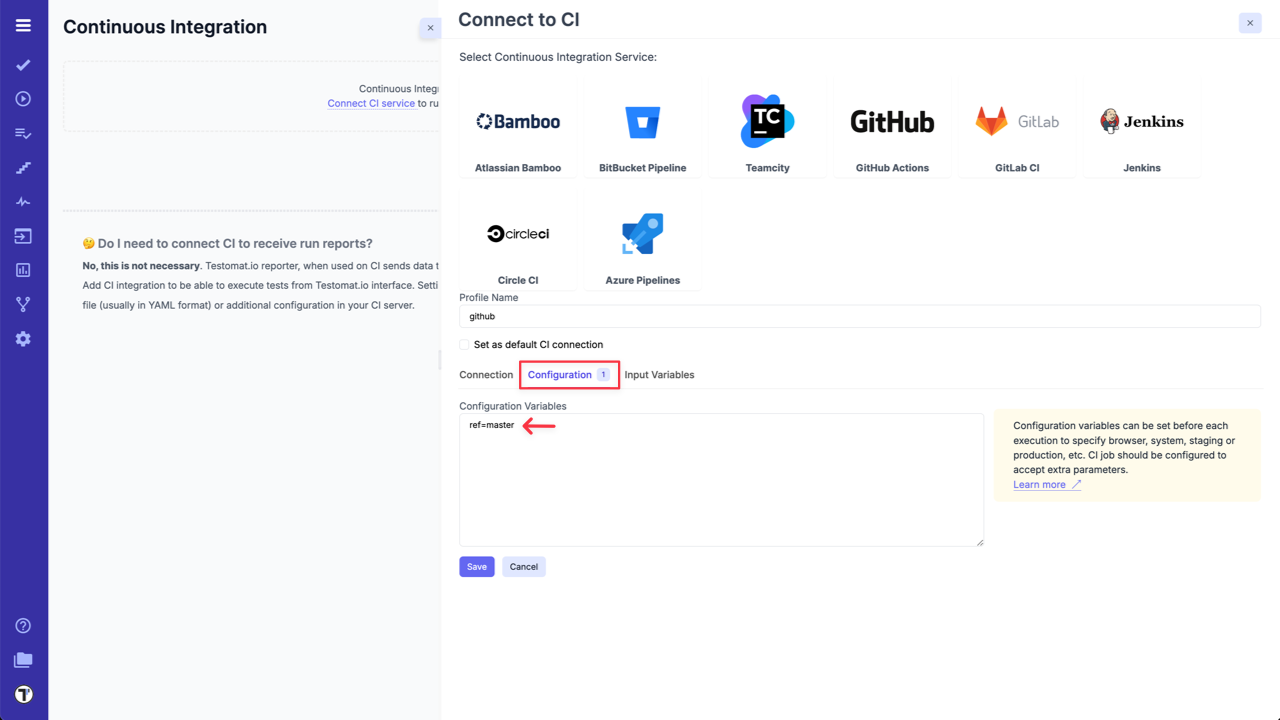
Config variables should be put per line with the default value passed in with =. The format is similar to .env file format:
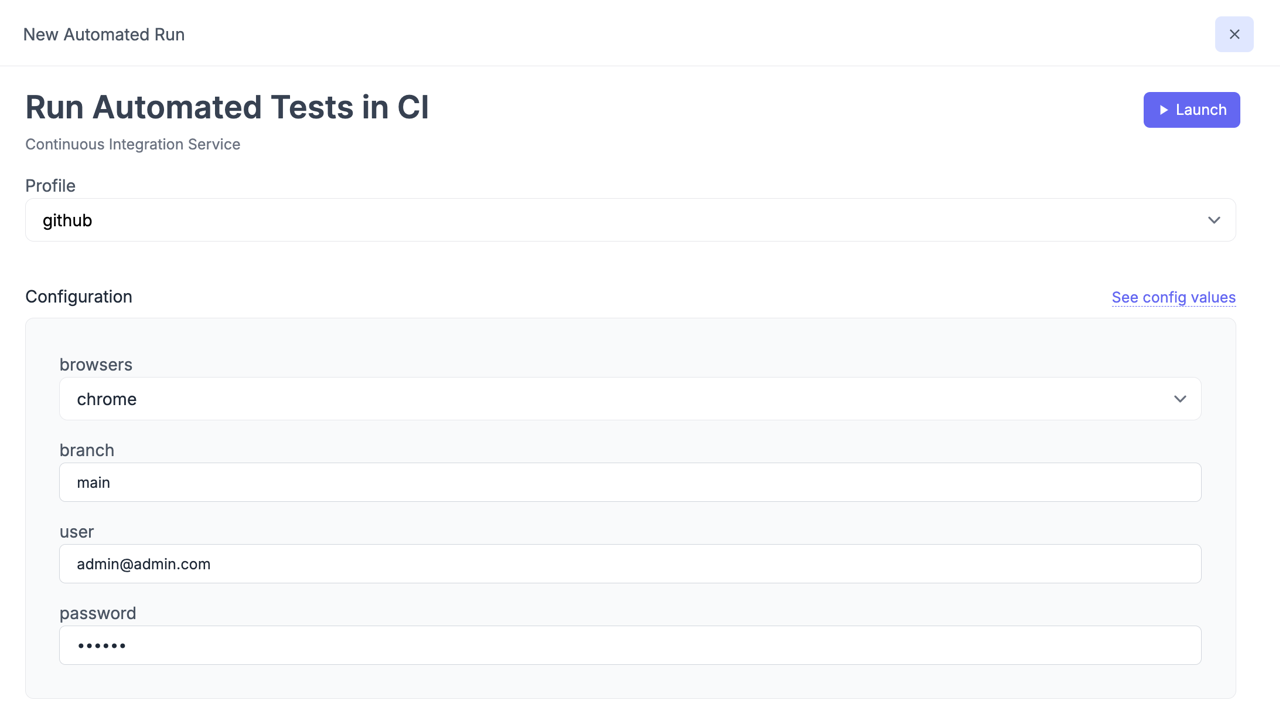
browsers=chrome,firefox,safaribranch=mainuser=admin@admin.compassword=123456suites=[3f4290f0,b89df296,78b10b62]ref=master config variable is set up by default for some CI services in Testomat.io but it can be changed at any time.
Those variables will be available for a reconfiguration on each CI Run executed from Testomat.io.
If a variable value contains comma , like in example above: chrome,firefox,safari, these values will be displayed with the select box. Otherwise, a simple input will be shown.
These variables will be passed to CI in the same manner as grep parameter. So, CI job should be prepared to handle these config variables. For instance, if GitHub Actions are used, values are passed as inputs and can be used like this:
- run: npx codeceptjs run --grep "${{ github.event.inputs.grep }}" --profile "${{ github.event.inputs.branch }}" env: TESTOMATIO: "${{ github.event.inputs.testomatio }}" # passed from Testomatio by default BROWSER: "${{ github.event.inputs.browser }}" TEST_USER: "${{ github.event.inputs.user }}" TEST_PASSWORD: "${{ github.event.inputs.password }}"Assigning IDs
Section titled “Assigning IDs”To execute a specific test or a suite a test runner should have a way to find a test by its unique name. For this reason, Testomat.io IDs can be used. If tests in the source code will have Testomat.io IDs it will be very simple to filter tests. We provide a semi-automatic way to assign Testomat.io IDs to tests in source code.
For JavaScript frameworks use the same check-tests command you used for importing tests with --update-ids. The tests must be already imported in Testomat.io:
TESTOMATIO={apiKey} npx check-tests <framework> <pattern> --update-idsFor Cucumber tests use check-cucumber command with the similar --update-ids command. The command should be the same as for importing plus --update-ids option:
TESTOMATIO={apiKey} npx check-cucumber <pattern> --update-idsThis command will update your source code. Please check the changes before committing it. If the Testomat.io IDs were placed correctly you can commit your changes to repository.
From now on, Testomat.io can use Test IDs to run exact tests and suites on Continuous Integration servers.